
Then, these predicted values are compared with the actual value and the difference (error) is what gets sent to the next stage for encoding. PX and PY are the predicted X and Y X -1is the previous X value X -2 is the X value two backĪs an example, if X = (2, 8, 24, ?) PX = (2 * X -1) - X -2 = (2 * 24) - 8 = 40.Here is a sample using simple linear algebra:
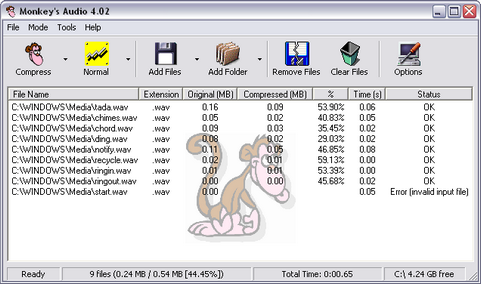
There are virtually countless ways to do this. This stage is what separates one compression scheme from another. Next, the X and Y data is passed through a predictor to attempt to remove any redundancy.īasically, the goal of this stage is to make the X and Y arrays contain the smallest possible values while still remaining decompressible.

The mid (X) is the midpoint between the L and R channels and the side (Y) is the difference in the channels. In this case, a mid (X) and a side (Y) value are encoded instead of a L and a R value.
There is often a great deal of correlation between the L and R channels, and this can be exploited several ways, with one popular way being through the use of mid / side encoding. The first step in lossless compression is to more efficiently model the channels L and R as some X and Y values. Lossless compression can be broken down into a few basic steps.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
